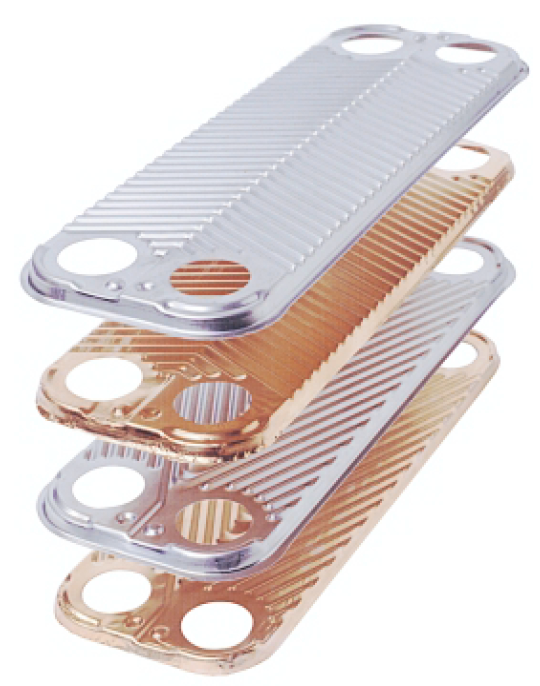
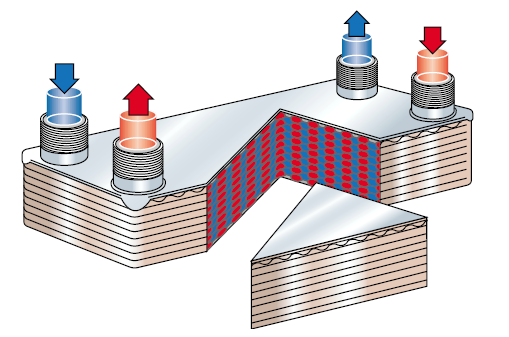
Plate design
The heat transfer surface of the Brazed Heat Exchanger (BHE) consists of thin corrugated AISI 316 plates.
The corrugation of the plates increases the heat transfer surface and can be made in various geometrical patterns. These patterns will, when two plates are put together, form a complex interplate channel promoting high turbulence of a fluid passing through the channel. They will also make it possible to create different channels optimised to meet the customer's duty and pressure drop requirements. Further the corrugation provides a multitude of contact points between the two plates.
The design of the plate periphery is made to avoid sharp edges that could cause damage when handling.

Channel design
Plates are stacked to form a plate pack which is covered by cover plates. Connections can be located in the front and/ or rear cover plate. During the brazing process, the capillary forces will collect the brazing material at the contact points between the plates.
The multitude of contact points across the plate surface makes the plate pack rigid. In fact, when approving the design of each BHE type, the pressure vessel authorities require Alfa Laval to test the units at five times the design pressure. Along with plate corrugation, the contact points create a turbulent media flow through the channels. This turbulent flow, and in general heat transfer through thin plates, is an exceptionally efficient method of heat exchange.

Compact and tough
The brazed plate heat exchanger is extremely compact. This compactness is achieved by:
• high heat transfer coefficients
• small hold-up volume
• use of thin material
The stainless steel plates are brazed to a package with copper or nickel as brazing material.
This means that the package becomes extremely strong, withstanding temperatures of up to 225 °C and pressures of up to 30 bar for copper brazed units. The nickel brazed units can withstand temperatures up to 400 °C and pressures of up to 16 bar.

Low weight
A brazed plate heat exchanger weighs only 20-30% of a shell & tube heat exchanger for the same cooling duty.
Easy installation
The rectangular and compact shape and front positioned connections make the unit easy to install or fit to any package or skid. Connections on the rear side are also available if required.
Low water consumption
The thermally efficient design reduces operating costs. It is possible to downsize the system components and use less energy to operate the system. For example the brazed heat exchanger uses down to a third of the water flow in a shell & tube heat exchanger for the same cooling duty. If there is a need to reduce media volume e.g. if the media are expensive (glycol) or enviromentally harmful (freons) the small hold- up volume is even more valuable.

Durable
The durable design makes the unit less vulnerable to vibrations and more resistant to high temperature and pressure. There are no gaskets in a brazed plate heat exchanger, and the risk of leakage between the media is thus practically eliminated.
Corrosion resistant
All parts of the brazed plate heat exchanger are made in AISI 316 stainless steel plates, which guarantees a much higher corrosion resistance as opposed to a carbon steel shell.
Low fouling
The corrugated plates induce a highly turbulent flow. The scrubbing action of the turbulence reduces build-up in the heat exchanger to a minimum. If cleaning is needed, the unit can be backflushed to remove debris or chemically cleaned to remove scale build-up.




 009821-88934322
009821-88934322



